Internet Data Centers: The Backbone of Global Data Exchange
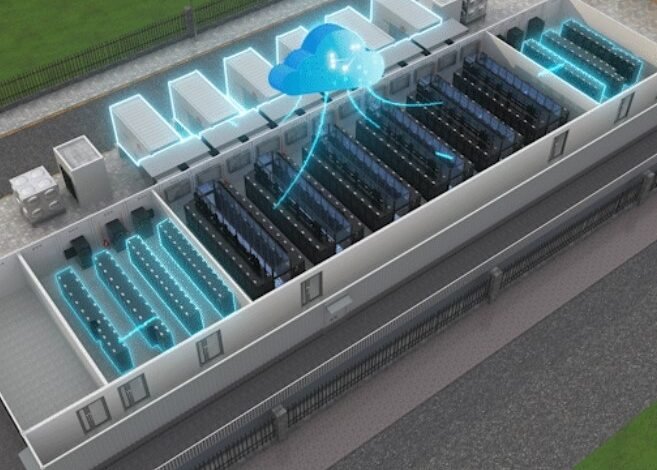
Internet data centers are essential for global data exchange, powering online activities from web browsing to complex transactions. These facilities house critical computing infrastructure, ensuring data availability and integrity. They support everything from e-commerce to financial services, enabling businesses to operate efficiently. This guide explores how data centers power the digital economy, support global connectivity, and drive sustainability efforts while addressing challenges for future growth and security.
How Internet Data Centers Power the Digital Economy
The Role of Data Centers in Cloud Computing
Data centers support cloud computing by storing and processing data for cloud services. Major companies use data centers to offer scalable services, improving cost-efficiency and reliability. These centers ensure high availability and redundancy, enabling businesses to access resources on-demand, and fostering innovation and agility in the digital economy.
See also: Vacuum Smarter, Not Harder: The Advantages of Cordless Technology
Enabling Real-Time Data Access for Businesses
Data centers provide real-time data access, vital for industries like finance and e-commerce. This infrastructure ensures instantaneous data availability, empowering businesses to make informed decisions quickly and stay competitive. High-speed networks and advanced storage systems enable seamless access, improving customer service and operational efficiency across industries.
Supporting High-Traffic Websites and Platforms
Data centers manage high-traffic volumes for platforms like social media and e-commerce sites. They provide powerful servers, storage, and networking capabilities to handle peak demands. Redundancy measures, such as backup power and multiple connections, ensure continuous service, crucial for maintaining performance and user satisfaction during high-traffic periods.
Enhancing the Internet of Things (IoT)
Data centers are crucial for IoT, managing vast amounts of data from connected devices. Edge computing enhances this by processing data closer to the source, reducing latency, and improving responsiveness. This combination drives the efficiency of smart systems, from home automation to industrial applications, enabling seamless operations and real-time analytics.
Key Components of Internet Data Centers
Data Center Infrastructure
Data centers are built around servers, storage systems, and networking equipment that manage and store data. Cooling systems and power supply units ensure smooth operation, while advanced monitoring tools track performance. These components enable high availability, scalability, and security, forming the backbone of modern digital infrastructure.

Physical Facilities and Redundancy
Data centers are designed with redundancy to ensure uninterrupted service. They feature multiple power sources, backup generators, and network connections to avoid downtime. Physical security, such as surveillance and access controls, along with environmental safeguards, protect critical equipment, ensuring data remains secure and services stay operational.
Data Center Security
Data centers deploy rigorous security measures, including physical access control, surveillance, and cybersecurity tools. Advanced encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection protect against data breaches. Regular security audits and disaster recovery plans ensure data integrity and continuity. These protocols safeguard sensitive information and maintain customer trust.
The Role of Data Centers in Global Connectivity
Data Centers as Global Hubs
Data centers serve as global hubs, connecting regions and enabling international data exchange. By hosting essential services and applications, they ensure seamless data flow across continents. Strategic placement of data centers reduces latency, improving performance for multinational companies and global users, and enhancing the digital experience.
Internet Backbone and Data Routing
Data centers house critical routers and switches, directing traffic across the internet’s backbone. They ensure efficient data routing through algorithms that determine optimal paths. This infrastructure allows fast, reliable data transmission, supporting communication and data exchange globally.
Content Delivery and Reduced Latency
Data centers help reduce latency by caching content close to end-users through content delivery networks (CDNs). This improves load times for websites and media, crucial for streaming services and e-commerce platforms. Strategically placed data centers ensure optimal performance, enhancing user experience and minimizing server load.
Why Sustainability Matters in Internet Data Centers
The Environmental Impact of Data Centers
Data centers consume significant energy, contributing to carbon emissions. The need for sustainable practices is increasing, as demand for digital services grows. Reducing energy usage, adopting green technologies, and using renewable energy sources are essential to mitigating environmental impact and ensuring sustainability in the digital sector.
Green Technologies in Data Centers
Data centers use green technologies to reduce energy consumption, such as liquid cooling, energy-efficient hardware, and solar power. Virtualization reduces the need for physical servers, cutting energy use. These technologies improve sustainability, reduce operational costs, and enhance the overall efficiency of data centers.
Renewable Energy and Carbon Neutrality
To reduce their environmental footprint, data centers are increasingly powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind. Many companies aim for carbon neutrality by purchasing renewable energy certificates (RECs). These initiatives significantly cut greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a more sustainable future for digital infrastructure.
Challenges Faced by Internet Data Centers and the Future
Scalability and Growing Data Needs
As data usage increases, data centers must scale their infrastructure. This requires investing in new hardware, expanding storage, and enhancing network capabilities. Data centers must adapt to handle larger volumes of data while remaining efficient and sustainable to meet future demand.
Security Risks and Solutions
As digital reliance grows, so do security threats to data centers. Cyberattacks and physical security breaches are significant risks. Data centers address these with encryption, firewalls, multi-factor authentication, and surveillance. Regular audits and compliance with standards help protect data integrity and ensure security.
Edge Computing and Its Impact on Data Centers
Edge computing, which processes data closer to its source, reduces latency and bandwidth usage. Data centers are adapting by integrating edge computing, and establishing smaller centers near users. This decentralized approach enhances real-time data processing and supports IoT applications, driving greater efficiency and performance.
Conclusion
The Internet data center is vital to the digital age, enabling cloud computing, real-time access, and high-traffic platforms. Their infrastructure, security measures, and global reach support seamless connectivity. Sustainability is becoming more important, with green technologies and renewable energy sources helping reduce their environmental impact. Data centers face challenges like scalability and security but will continue to evolve to meet growing data demands, ensuring a sustainable, secure future for the digital